
There has been a lot of hype around the advent of “AI in radiology”. Pioneers in the field of radiology believe that AI will make irreversible changes in medical imaging that will be beneficial for both physicians and patients, as well as healthcare providers.
The use of AI in the healthcare industry dates back to as early as the 1970s. In radiology, AI came to light in the form of Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD). Invented in the early 1980s, CAD became prevalent among radiologists only in the 1990s during the second wave of AI. Despite being AI-driven CAD was unable to meet users’ expectations at that time. As technology is well-known to evolve, AI has also come a long since its inception in the medical world.

After a roller coaster of setbacks and success, the current version of AI can supersede human capabilities in numerous aspects, particularly in the field of medicine and radiology. Unlike the initial versions of AI, the third wave of AI (deep learning) that can create self-thinking machines is changing dimensions and imaging diagnosis. Here’s a brief overview of it.
AI redefining medical imaging and diagnosis
Diagnostic imaging is considered to be one of the most promising clinical applications of AI. And for radiologists, medical imaging is part of their everyday routine.
A radiologist’s job is not just as easy or interesting as it sounds or is neither confined to just reading images and reporting findings. Apart from reading hundreds of images every day, radiologists perform numerous mundane tasks like sorting images, prioritizing cases, and reviewing information collected from diagnostic imaging procedures, including patient-facing work like ultrasound, biopsy, fluoroscopy, etc.
The increased challenges and workload in the field of radiology, and the ratcheting need for precision to reduce diagnostic errors have bred the need for automation to ease radiologists’ jobs and improve diagnosis.
The potential applications of AI in medical imaging range from data acquisition to image reconstruction and image analysis to predicting survival rates; applications that can not only lighten the load on radiologists with automation but also enable quick diagnosis and early intervention.
Future of Radiologists in the world of AI
AI is likely to refine radiology workflow with automation and boost radiologists’ performance in diagnosing diseases and handling volumetric imaging data.
With AI handling image -acquisition, reconstruction, screening, etc, for almost all the advanced imaging modalities (MRI, CT scan, PET), radiologists will have adequate time to study the pathologies and the underlying correlation between them.
Here’s how AI will alter radiologists’ universe:
1. Automation-aided quantitative analysis
Automation is the need of the hour for radiologists, given the increasing workload and associated risk of burnout. 90% of healthcare data, which is growing at an exponential rate, are images. Before diagnosing diseases from images, radiologists have to manually gather images from providers, perform a quality check on the images, and categorize the images into normal and abnormal ones.
Once the preliminary set of mundane tasks is done, there are a couple of other manual tasks that need to be performed based on part of the body and the type of imaging before looking for deformities/diseases.
Consider spine imaging – radiologists have to manually locate and label the different elements of the spine, and mark morphological points before eyeballing for deformities.
And since mundane tasks consume most of the radiologists’ productive hours, they are forced to analyze diseases and report them in a subjective manner, which is one of the primary reasons for incorrect treatment and complications during surgeries.
Quantitative analysis, which is deemed the best approach to diagnose problems at an early stage, particularly in the case of spine problems, can be effectively carried out with the help of AI.
AI can not only help in automating the preliminary set of mundane tasks but also can automatically identify and label body parts, quantify elements of the body part (spine, brain, etc.) and even generate quantitative reports.
Numerous AI tools are entering the radiology space to enable automation-aided quantitative analysis. Spindle, for instance, is an AI reporting tool for spine MRI, that can automatically identify deformities, quantify and characterize features of disc shape, detect signal intensity changes, grade disc degeneration, classify pathology in objective grades, etc, and generate quantitative reports in just a click.
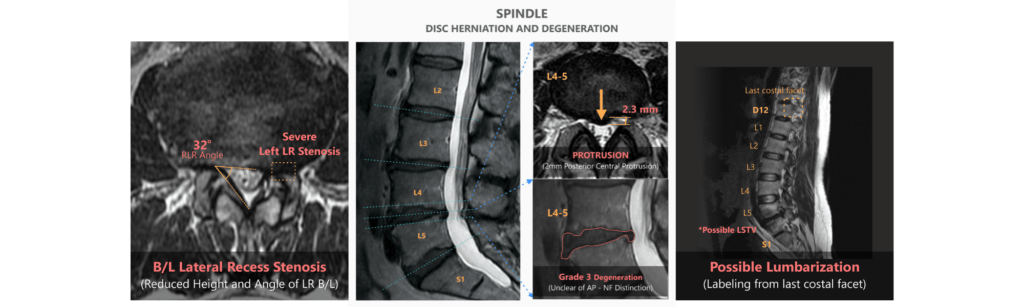
Spindle automates 70% of mundane tasks associated with spine MRIs, making diagnosis and radiologists’ lives much easier.
2. Predict risks and survival rates
Humans have always been keen to know the future, mostly to avoid unpleasant events. In the healthcare world, unpleasant outcomes can mean people losing their loved ones, or people confined to their bed for lifetime, which can be positively avoided if complications can be foreseen.
AI is making it possible to predict risks, survival rates, and post-operative care complications.
Experiments conducted at the University of Adelaide to predict patient mortality by analyzing CT scans showed that the AI model could predict which patient might die within the next 5 years with 69% accuracy.
Similarly, AI can be used to predict future illnesses. A recent study conducted to study AI’s potential in predicting the risk of heart attack from imaging techniques and clinical data proved that AI techniques can improve the prediction of heart attacks.
3. Automated Workflow Scheduling
Triaging, for a fact, is paramount for timely patient care. Similarly, prioritizing critical cases in imaging tests is essential to improve diagnosis speed and thereby appropriate treatment. AI can do a preliminary read on the imaging tests and prioritize the cases based on criticality. This not only saves radiologists’ time wasted on preparing workflow schedules but helps in the timely delivery of patient care.
Stats show that more than 60% of chest x-rays are normal in a clinical setting, and the lack of a prioritization protocol delays the reporting of critical studies. Crescent, an AI radiology software for Chest x-rays sorts abnormal images from normal one and prioritizes them in the worklist based on criticality. Such AI-enabled workflow scheduling not only enables timely reporting of critical cases but also improves reporting efficiency.
To Sum Up
AI is likely to be the new normal for radiologists in the next decade. AI has exhibited promising performance in medical imaging and related clinical applications. With AI to assist, radiologists can balance productivity and quality without sacrificing their health and personal time.
